1. 例子一
转自csdn博客

功能描述:
实现一个双输入,双输出,使用两个参数,使得输出为:
y1 = para1 * u1 + 5 y2 = para2 * u2 + 3
代码实现
代码如下:
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME test
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#define INPUT_NUM 2
#define OUTPUT_NUM 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include "simstruc.h"
#include <math.h>
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 2); /* Number of expected parameters */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
/* Return if number of expected != number of actual parameters */
return;
}
ssSetNumContStates(S, 0);
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 0);
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 2)) return;
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); /*direct input signal access*/
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 1, 1);
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 1, true);
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 1, 1);
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, OUTPUT_NUM)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 1, 1);
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 0.001);
ssSetNumRWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumIWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumPWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumModes(S, 0);
ssSetNumNonsampledZCs(S, 0);
/* Specify the sim state compliance to be same as a built-in block */
ssSetSimStateCompliance(S, USE_DEFAULT_SIM_STATE);
ssSetOptions(S, 0);
}
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, CONTINUOUS_SAMPLE_TIME);
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
}
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
real_T *para1 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 0));
real_T *para2 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 1));
const real_T *u1 = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0);
const real_T *u2 = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,1);
real_T *y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0);
real_T *y2 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,1);
y1[0] = para1[0]*u1[0] + 5;
y2[0] = para2[0]*u2[0] + 3;
}
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */
#endif
代码解析
1. 初始化
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 2); /* Number of expected parameters */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
/* Return if number of expected != number of actual parameters */
return;
}
ssSetNumContStates(S, 0);
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 0); //连续和离散状态个数都为0
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 2)) return;//2个输入
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 1); //1号输入的宽度为1,即维数为1
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); /*direct input signal access*/
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 1, 1); //2号输入的维数也为1
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 1, true);
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 1, 1);
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, OUTPUT_NUM)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1); //1号输出的维数为1
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 1, 1); //2号输出的维数为1
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 0.001); //采样时间
ssSetNumRWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumIWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumPWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumModes(S, 0);
ssSetNumNonsampledZCs(S, 0);
/* Specify the sim state compliance to be same as a built-in block */
ssSetSimStateCompliance(S, USE_DEFAULT_SIM_STATE);
ssSetOptions(S, 0);
}
2. 控制算法
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
real_T *para1 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 0)); //获得参数1
real_T *para2 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 1)); //获得参数2
const real_T *u1 = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0); //获得输入u1
const real_T *u2 = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,1); //获得输入u2
real_T *y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0); //输出y1
real_T *y2 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,1); //输出y2
y1[0] = para1[0]*u1[0] + 5; //输出与输入关系
y2[0] = para2[0]*u2[0] + 3;
}
最后,使用mex 文件名.c编译,使用simulink s-function模块,将保存在同一文件夹下的模型名填入,仿真即可。
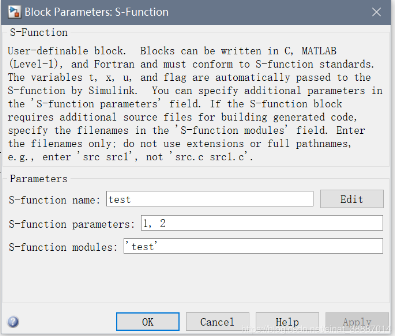
对于输入都为1,参数分别为1,2,其输出结果:
2. 例子二
转自博客园

2.1 MATLAB配置
1.先配置一下 mex -setup
mex -setup Please choose your compiler for building external interface (MEX) files:
Would you like mex to locate installed compilers [y]/n? mex -setup
Select a compiler: [1] Borland C++Builder version 6.0 in D:\soft\c++builer [2] Lcc C version 2.4 in D:\MATLAB\sys\lcc [3] Microsoft Visual C/C++ version 6.0 in D:\soft\viual c++
[0] None
Compiler: 2
Please verify your choices:
Compiler: Lcc C 2.4 Location: D:\MATLAB\sys\lcc
Are these correct?([y]/n): y
Try to update options file: C:\Documents and Settings\zjj\Application Data\MathWorks\MATLAB\R14\mexopts.bat From template: D:\MATLAB\BIN\WIN32\mexopts\lccopts.bat
Done . . .
2.打开viual c++ ,新建文本文件,编写s-function,保存Text1.c
3.在matlab中mex Text1.c
4.在simulink中拖出一个s-function模块,改名为Text.c
补充:封装和测试步骤
编好S - 函数后,对相应的模块进行封装和测试: 1)向模型窗口中加入S-function 模块,双击该模块,打开参数设置对话框(Block Parameters),输入 源文件名和用户定义的参数表; 2)选择该模块,按Ctrl + M,打开封装编辑器(Mask Editor)。在Mask type 编辑框中输入模块类型 名;在Icon 页中用MATLAB 的有关绘图命令绘制模块图标;在Initialization 页中添加用户定义的变量 参数,必要时对变量初始化;在Documentation 页中添加模块的说明和帮助文档。 3)给模块命名; 4)建立一个简单仿真模型框图,测试模块功能。
2.2 MATLAB中的S-Function的用法(C语言)
-
S-Function简介
S-Function是system-function的缩写。说得简单,S-Function就是用MATLAB所提供的模型不能完全满足用户,而提供给用户自己编写程序来满足自己要求模型的接口。 -
MEX函数与M文件的区别 第一, MEX 函数能实现的回调函数比M-文件能实现的回调函数要多得多;
第二, MEX 函数直接访问内部数据结构SimStruct,SimStruct 是Simulink 用来保存关于S-function 信息的一个数据结构;
第三, MEX 函数也可使用MATLAB MEX 文件API 直接来访问MATLAB 的工作空间。
如果一个C MEX文件与一个M文件具有相同的名字,则C MEX文件被优先使用,即在S-Function块中使用的是C MEX文件。
- 基础知识 3.1 直接馈通(direct feedthrough) 直接馈通表示系统的输出或可变采样时间是否受到输入的控制。
a. 输出函数(mdlOutputs或flag==3)是输入u的函数。即,如果输入u在mdlOutputs中被访问,则存在直接馈通。
b. 对于一个变步长S-Function的“下一个采样时间”函数(mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit或flag==4)中可以访问输入u。
例如,一个需要其输入的系统(也就是具有直接馈通)是运算y=kXu,其中,u是输入,k是增益,y是输出。
又如,一个不需要其输入的系统(也就是没有直馈通)是一种简单的积分运算:
输出:y=x;
导数:dx/dt=u
其中,x是状态,dx/dt是状态对时间的导数,u是输入,y是输出。
正确设置直接馈通标志是十分重要的,因为它影响模型中块的执行顺序,并可用检测代数环。
3.2 dynamically sized inputs 主要是给出:输入连续状态数目(size.NumContStates),离散状态数目(size.NumDiscStates) ,输出数目(size.NumOutputs),输入数目(size.NumInputs),Direct Feedthrough(size.Dir Feedthrough)。
3.3 setting sample times and offsets setting smaple times and offsets主要设置采样时间.
3.4 Level-1 和Level-2 Level 1 提供一个简单的接口,可与少部分的S函数API交互。Matlab对于这种方式的支持更多的是为了保持与以前版本的兼容,现在推荐采用的是Level 2 S函数。
- S-Function实例
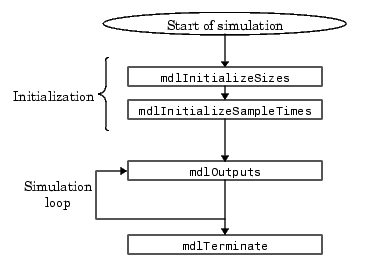
S-Function的仿真流程
例如要创建一个有1输入(2维),2输出(1维),3个参数,还有全局变量的S-Function。 过程如下:
a. 新建sfunction的C语言文件
打开simulink,点击User-Defined Functions里面的S-Function Examples。这个里面有多个语言版本的模板,有C,C++,Ada,Fortran和M语言的版本,其实都大同小异,只要了解几个函数就很容易使用了。 选择C语言的版本:从S-function模块中选择C-file S-functions里面的Basic C-MEX template。打开后,另存为自己的模块名字,如test.c 。下面我们来分析代码:
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME test//这里把文件名sfuntmpl_basic修改为test
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#include "simstruc.h"
//程序里面要用到的头文件在这里引用,如“math.h”等。
float global_var; //定义全局变量
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
//这个函数用来设置输入、输出和参数的。
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 3); /*设置参数个数,这里为3 */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
return;
}
ssSetNumContStates(S, 0);//设置连续状态的个数,缺省为0;
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 0);//设置离散状态的个数,缺省为0;
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return;//设置输入变量的个数,这里为1
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 2); //设置输入变量0的维数为2
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); //设置input0的访问方式,true就是临近访问,这样指针的增量后就可以直接访问下个input端口了。
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);// 设置输入端口的信号是否mdlOutputs函数中使用,这儿设置为true。
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 2)) return;//设置输出变量的个数
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);//设置输出变量0的维数为1维
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 1, 1);//设置输出变量1的维数为1维
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1); //设置采样时间,此处为1s。
ssSetNumRWork(S, 0);//不管
ssSetNumIWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumPWork(S, 0);
ssSetNumModes(S, 0);
ssSetNumNonsampledZCs(S, 0);
ssSetOptions(S, 0);
//下面可以写全局变量的初始化程序
global_var=1;
}
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)//暂时不管
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, CONTINUOUS_SAMPLE_TIME);
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
}
#define MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS)
static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)//暂时不管
{
}
#endif /* MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS */
#define MDL_START /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_START)
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)//暂时不管
{
}
#endif /* MDL_START */
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)//这里填入相关的运算、算法等
{
real_T *para1 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,0));
real_T *para2 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,1));
real_T *para3 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,2));
const real_T *u = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0);
real_T *y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0);
real_T *y2 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,1);
y1[0]=u[0]*para1[0]+u[1]*para2[0];
y2[0]=u[1]*para3[0]+u[0]*para1[0];
}
#define MDL_UPDATE /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_UPDATE)
static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_UPDATE */
#define MDL_DERIVATIVES /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_DERIVATIVES)
static void mdlDerivatives(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_DERIVATIVES */
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)//这里需要把global变量全部初始化,否则下次运行程序时,全局变量还是之前的值。
{
}
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */
#endif
b. 编译
在matlab的command window 里面输入“mex test.c”,即可将test.c编译为mex文件。
c.调用sfunction
在simulink空间里面拉入sfunction,在s-function name里面填入test,参数里面填入要设定的参数,然后仿真即可。
总结
整体结构并不复杂,但是,如何使用C语言进行算法编程是难点。
比如
real_T *para1 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,0));
mxGetPr这样的命令如何获取,指针的操作如何进行,数据类型如何定义,如何求微分方程,如何调用.mat文件。